Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Kubernetes and OpenShift both excel in simplifying container orchestration. Their superior performance and rapid deployment have gained popularity in businesses worldwide. Both these tools portray similar characteristics which is pretty obvious as Kubernetes is a fundamental component of OpenShift architecture. Though their primary objectives set them apart. Today, in this article, we will explore its benefits and key differences
What is Kubernetes?
It is a container as a service (CaaS) open-source software used by organizations for automation, deployment, and management of application workloads. Kubernetes was created by Google in 2014 and later developed by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation using the Go language. Kubernetes components come in the form of a cluster when deployed from its official website.
Key Features of Kubernetes
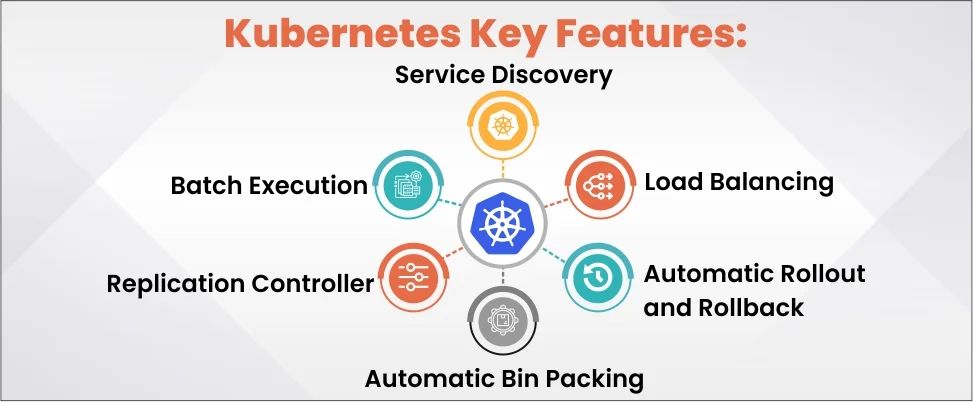
- Service Discovery: This feature automatically assigns DNS names, IP addresses, and load balances to Pod. This gives easy access to locating and connecting to this Pod.
- Load Balancing: It helps to create a balance between the traffic across various pods that provide equal services. By doing this, the application runs smoothly and plays an essential part in locating services. Developers can use this to connect with the outside world or between the pods using the same IP address.
- Automatic Rollout and Rollback: This feature acts as a safety shield against system failure. Whenever it detects any issue or fault in the application it automatically rolls back to the previous version that was working correctly. Thereby reducing downtime and maintaining the stability of the application.
- Automatic Bin Packing: It efficiently arranges containers based on their resource requirement. This also optimizes resource usage and reduces wastage of resources.
- Replication Controller: It ensures that Kubernetes pods are always available at all times. If it encounters pods that are more than what is specified, then it gets rid of those extra pods. And if there are requirements for more, then it creates some more. Unlike, the manual this automatic replication deletes or replaces if they are deleted or terminated.
- Batch Execution: It gives control to run and expand programs in Kubernetes. Developers can either do it manually or automatically handle tasks to run batches and manage CI workloads.
Pros & Cons of Kubernetes
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Free to use | Poor container image management |
| Automatic rollback and rollout handle downtime efficiently | Monitoring across the cluster can be challenging |
| Flexibility | Complex UI/td> |
| Default dashboard | Security issues |
| Load balancing capabilities | Challenging to understand containers |
| Supports many programming languages and framework | Lack of in-built tools |
| Uses infrastructure resources efficiently | Dependency on other resources |
| Large active community | Reliance on experience |
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best!
Apply for top job opportunities today!
What is OpenShift?
OpenShift is an open-source enterprise-grade platform written in Go and AngularJS. It is mainly used for container application development. It supports other programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, Go, and Node.js. Besides, it can easily integrate with DevOps tools, making it a great tool for large-scale and small-scale enterprises.
Key Features of OpenShift

- Cluster installation and Upgrades: The installer-provisioned architecture gives full control to the AWS installation process. This particular feature speeds up the process of cluster creation from the initial stage. On one hand, the upgrade feature simplifies the UI administration to track availability updates for clusters.
- Knative: The usage of Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) in OpenShift 4 manages the management, deployment, and development of a serverless function. This particular feature adapts to the changes in demand, making applications more efficient and cost-effective.
- OOD Command Line Interface: This makes the developer task way easier to containerize their code and deploy it on OpenShift. It simplifies the process and ensures applications are running on the platform.
- Cloud Automation: Offers virtual platforms for OpenStack, Red Hat Virtualization, VMware, and Premises bare metal.
- Kubernetes Operators: This feature is the new one added to the OpenShift that aids in managing applications. This allows code to work with the Kubernetes in a more dynamic and efficient manner. It can also take on various tasks such as scaling complex apps, new software version updates, and maintaining node modules in hardware clusters.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The hybrid infrastructure simplifies the deployment by allowing it to run on-premise or in the cloud. In a matter of seconds, it can scale up to a thousand instances across hundreds of nodes.
Pros & Cons of OpenShift
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Supports container initiative (OCI) to host and run | Challenging to manage cluster logs |
| Can be easily used with the cloud provider or on-premises | Not flexible |
| Simple UI and UX | Hard to understand |
| Third-party plugins for every release | Small community |
| Supports Prometheus and Grafana to monitor cluster | Limit up to120 compute nodes and 3,00,000 pods |
| Many remedies for security, performance issues, and defects | Expensive |
| Deploys application faster | Limited support and frameworks |
| Quick implement and enforce policies | Many components increase complexity |
OpenShift vs Kubernetes:Technical Difference
Although Kubernetes and OpenShift have a resemblance in their traits, their primary objectives are entirely different. The table below outlines the major differences of these two:
| Kubernetes | OpenShift | |
|---|---|---|
| Image Registry | No image registry | Integrated image registry used with Red Hat or Docker Hub |
| Security | Complex configuration setup makes it vulnerable to security threat | Default security features |
| Deployment | Kubernetes deployment is Implemented using controllers | OpenShift is deployed using a command |
| Networking | No native networking solution | It provides Open Switch for native networking solution |
| Update and Support | No customer service | Good customer service |
| Integrated CI/CD | It relies on CI/CD flow | Does not mandate on CI/CD pipeline |
| Cloud-Platform | GKE for Google GCP, AKS for Microsoft Azure, and EKS for Amazon AWS | Openshift online and Openshift Azure |
| Multiple Support | Supports | Does not support |
| Open-source | Open-source | Subscription-based |
| Helm | Uses set of YAML | It lacks Helm |
| Built-in/Third-Party | Relies on third-party | Monitoring and Networking by default |
| Base | Runs on different OS and platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure | Red Hat Enterprise Linux or RHEL, CentOS, and Fedora |
| Rollout | Provides extensive solutions to create clusters | Does not require additional components |
| Dashboard | Hard-to-operate interface | Great user experience |
| Learning Curve | Complicated web consoles make it hard for beginners | Ideal for beginners |
| Organization Usage | Deutsche Bank, Intermountain Healthcare, Optus, ThoughtWorks, BMW, Worldpay Inc., and HCA Healthcare | IBM, Phillips, Nokia, Spotify, NAV, China Unicom, Bose, Amadeus, Comcast, Anti-financial, eBay, and AppDirect |
Kubernetes vs. OpenShift: Which One is the Best?
You need to balance the pros and cons to make a choice between these containerization tools. It is not fair to say that one is superior to the other because both of these tools offer excellent containerization mechanisms.
OpenShift does not come free and you may need to cough up some cash as you scale up your cluster.
Whereas, with Kubernetes, you don’t need to empty your wallet! It’s free to download and available on GitHub. So, keeping all this in mind, you can make a wise choice. All in all, both the tools are great and offer the best of strengths, you won’t be disappointed with either.
Benefits of Choosing OpenShift over Kubernetes
Openshift offers a remarkable option for ImageStream and indeed, its rich feature helps in the creation and management of container apps. Plus, the simplistic design and testing of the application make Openshift a top-tier platform in the industry.
Benefits of Choosing Kubernetes over OpenShift
As mentioned before, Kubernetes is cost-effective with a strong customer support and great productivity. In comparison to other containerization tools, it provides more budget-friendly options.
Kubernetes also gets support from the leading cloud providers and active community. As a result, its ecosystem extends lot of benefits from the regular updates and releases.
Final words
Now that you know the difference between Kubernetes and Openshift, these both are in high demand in the IT industry. You can choose Kubernetes if you are looking for flexibility or else go for Openshift for easy deployment and management of container orchestration.
FAQs
Openshift updates pods using deployment configuration but doesn’t support concurrent updates while Kubernetes is a more versatile option for scaling with concurrent updates. Besides, Openshift runs on limited operating systems, and Kubernetes can run and install on various OS.
No, it’s not. Kubernetes is free and easily downloaded from GitHub. However, Openshift is subscription-based and is associated with cluster size meaning as the cluster size increases your cost keeps getting higher.
Kubernetes needs to install the Kubernetes dashboard and manual token creation authentication. Whereas Openshift provides straightforward administration of clusters on a web-based.
Yes, there is because Kubernetes keeps frequently releasing and updating. While Openshift has fewer updates and releases.
In terms of security, Openshift offers strong and strict security features by restricting the running containers as root.
Take control of your career and land your dream job!
Sign up and start applying to the best opportunities!


