Table of Contents
ToggleCybersecurity has become a critical issue for businesses and individuals alike in recent years. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated and frequent, the demand for professionals keen on starting a career in cybersecurity is on the rise. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics expects the number of cybersecurity positions to increase by 33% from 2020 to 2030. This demand has increased even more because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In this blog post, we will outline the steps you can take to start a career in Cybersecurity in 2023.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting electronic devices, networks, and sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, damage, or disruption. It involves the use of technology, processes, and policies to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
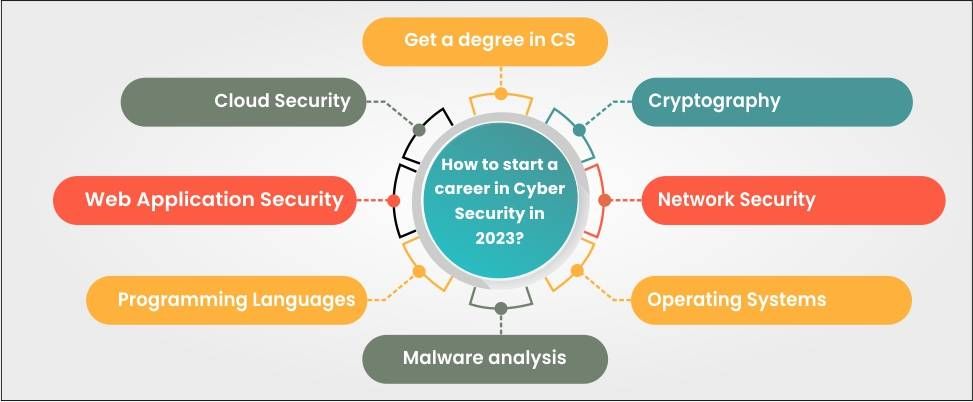
How to start a career in Cyber Security?
To start a career in cybersecurity, you will need to have a deep understanding of a range of technical skills. Some of the key technical skills required to start a career in cybersecurity include:
- A degree in computer science: Although having a degree is not mandatory to thrive in a cybersecurity career, it can assist you in establishing a robust groundwork. According to a survey, 8% of professionals reported having only a high school diploma. Pursuing a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer science or a relevant area may allow you to waive some work experience requirements for obtaining prestigious certifications.
- Network security: A good understanding of networking protocols and architecture, as well as knowledge of network security tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
- Operating systems: A strong knowledge of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and MacOS is important. This should include knowledge of system configuration, hardening, and patch management.
- Cryptography: A good understanding of encryption, decryption, and digital signatures. Knowledge of cryptographic protocols such as SSL/TLS and SSH is also important.
- Malware analysis: The ability to analyze and reverse-engineer malware to identify its behavior and potential impact on systems and networks is important.
- Programming languages: Knowledge of programming languages such as Python, C++, and Java can be helpful in developing security tools and automating security tasks.
- Web application security: Knowledge of web application security, including common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS), and knowledge of web application security testing tools.
- Cloud security: Knowledge of cloud security concepts and technologies, including cloud-specific security risks, access controls, and data protection is a must.
- Incident response: Knowledge of incident response methodologies and tools, including incident detection, analysis, containment, and remediation
What are the other skills required to start a Career in Cybersecurity?
- Technical knowledge: To start a career in cybersecurity, you should have a deep understanding of computer networks, operating systems, programming languages, and security technologies like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Threat intelligence: You should be familiar with the latest cyber threats and vulnerabilities and be able to analyze and interpret threat intelligence data to identify potential risks.
- Analytical skills: You should be able to analyze and interpret large amounts of data, identify patterns, and develop strategies to prevent or mitigate potential threats.
- Communication skills: You should be able to communicate complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders and be able to collaborate effectively with other cybersecurity professionals, IT staff, and business leaders.
- Problem-solving skills: You should be able to think critically and creatively to solve complex cybersecurity problems and be able to develop and implement innovative solutions to protect against cyber threats.
- Ethical hacking skills: You should be able to think like a hacker and use ethical hacking techniques to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
- Risk management skills: You should be able to assess and manage risks to digital assets and develop and implement policies and procedures to minimize the risk of cyber-attacks.
- Continuous learning: You should be committed to continuous learning and keeping up to date with the latest trends and developments in the cybersecurity field.
- Choose a specialty: There are many different areas of cybersecurity, so it’s essential to choose a specialty that aligns with your interests and skills. Some of the most popular specialties include network security, application security, cloud security, and ethical hacking.
- Get certified: Certifications are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and skills to potential employers. Some of the most widely recognized certifications in the cybersecurity industry include CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
- Gain experience: Experience is crucial in any field, and cybersecurity is no exception. Look for internships or entry-level positions that will allow you to gain hands-on experience in your chosen specialty. You can also participate in bug bounty programs or contribute to open-source projects to build your portfolio.
- Build a network: Networking is essential in any industry, and cybersecurity is no exception. Attend industry events and conferences, join online forums and social media groups, and connect with other cybersecurity professionals. Building a network can help you stay up to date on the latest trends and technologies and provide you with opportunities for career advancement.
- Stay up to date: Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, so it’s essential to stay up to date on the latest threats, technologies, and best practices. Read industry blogs and news sites, attend conferences and webinars, and participate in training programs to stay current.
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best
Apply for top global job opportunities today!
What are the job careers in Cybersecurity in 2023?
There are a variety of job careers available for professionals looking to start a career in cybersecurity, with different roles and responsibilities that cater to different skill sets and interests. Some of the common job careers in cybersecurity include:
Cybersecurity Analyst
- Average Salary: $81,689/year
- Cybersecurity Analysts are responsible for monitoring and analyzing security threats, investigating security incidents, and recommending solutions to improve security.
Cyber Security Engineer
- Average Salary: $92,292/year
- Security Engineer is responsible for designing and implementing security solutions to protect networks, systems, and applications from cyber-attacks.
Penetration Tester
- Average Salary: $90,595/year
- Penetration Tester is responsible for testing the security of networks, systems, and applications by simulating cyber-attacks to identify vulnerabilities and recommend remediation.
Incident Responder
- Average Salary: $46,580/year
- Incident Responder is responsible for detecting and responding to cyber incidents, including containment, eradication, and recovery.
Cybersecurity Consultant
- Average Salary: $59000 – $1,00,000/year
- Cyber Security Consultant is responsible for providing expert advice on cybersecurity risk management, compliance, and governance.
Cybersecurity Architect
- Average Salary: $154,989 per year or $74.51 per hour
- Cybersecurity Architect is responsible for designing and developing secure systems, networks, and applications.
Security Administrator
- Average Salary: ₹84525/year
- Security Administrator is responsible for managing and maintaining security systems and controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and access control systems.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Average Salary: $1,86,492
- CISO is responsible for managing an organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy and ensuring that cybersecurity risks are appropriately managed.
Source: Glassdoor
Career Path | Entry Level | Mid-Level | Advanced Level |
Job Titles | Security Analyst, Junior Security Engineer, Security Consultant | Senior Security Analyst, Security Engineer, Security Architect | Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Security Manager, Director of Security |
Key Skills | Basic understanding of security principles and concepts, knowledge of security tools and techniques, ability to analyze and interpret security data | In-depth understanding of security principles and concepts, strong technical skills in areas such as network security, application security, and cryptography, experience with security frameworks and standards | Leadership and strategic skills, ability to develop and implement security policies and procedures, experience with risk management and compliance |
Educational Requirements | Bachelor’s degree in computer science or related field, relevant certifications such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) | Bachelor’s degree in computer science or related field, relevant certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) | Master’s degree in computer science or related field, relevant certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) |
Job Responsibilities | Conducting security assessments, identifying, and analyzing security vulnerabilities, monitoring security events and incidents, implementing security controls | Developing and implementing security strategies and policies, designing, and implementing security solutions, leading security projects and initiatives, managing security operations | Developing and implementing enterprise-wide security programs, managing security budgets and resources, representing the organization in security-related matters |
Best Cybersecurity Companies to work with in 2023
1. Deloitte
Job openings
- SOC Analyst
- Data Engineer
- Data Scientist
- Operational Technology (OT) Engineer
- Cyber Requirements Analyst
- Advanced Cyber Threat Hunter
- RMF Analyst
- Cybersecurity Specialist (Security Control Assessor)
- Cybersecurity Specialist
- Information Systems Security Engineer
- Deloitte Risk & Financial Advisory Analyst – Cyber
- Deloitte Risk & Financial Advisory Intern – Cyber
For more: Visit Deloitte Jobs
2. Palo Alto Netwrks
Job openings
- Enterprise Security Engineer (Information Security)
- Senior Manager, Product Security
- Federal Cyber Architect
- Director Product Security
- Senior Consultant, Offensive Security, Proactive Services
- Principal Windows Security Researcher (Cortex)
- Senior Email Security Researcher (Cortex XDR)
- Principal Linux Security Researcher (Cortex XDR)
- Senior Threat Intelligence Analyst
For more: Visit Palo Alto Jobs
3. Microsoft
Job openings
- Senior Security Operations Engineer
- Senior Threat Intelligence Analyst
- Seniore Security Researcher
- Partner Research Director, IDC
For more: Visit Microsoft Jobs
4. Rapid7
- Vulnerability Management
- Security Consultant
- Senior Security Engineer
- Project Manager, Security Research
- Director, Security Operations and Engineering
For more: Visit Rapid7
5. Coalfire
Job Openings
- Security Engineer – ELK
- Security Engineer – Vulnerability Management
- Senior Compliance Advisor
- Senior Manager – Security Operations
- Senior Manager – Site Reliability Engineering
- Senior SIEM Engineer
- Site Reliability Engineer
- Senior Consultant – Application Security
6. Proofpoint
Job Openings
- Associate Security Solution Analyst
- Associate Triage Analyst
- Security Research Engineer
For more: Visit Proofpoint
7. Trellix
- Email Security Cloud – Sustenance Engineer
- Threat Intelligence – Security Researcher
- McAfee Endpoint Security Engineer
8. Booz Allen Hamilton
Job Openings
- Cyber Security Engineer, Lead
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Cyber and Communications Security Program Analyst
- Tier 2 Cyber Security Operations Center Analyst
- Cyber Intern
- Cyber Threat Specialist
- ICS OT Cyber Threat Intel Analyst
- Cyber Architect, Mid
- Cyber Architect, Senior
- Cyber Engineer, Lead
- Cyber Network Engineer, Senior
- Cyber Tools Assessor, Senior
- Cyber Defense Incident Responder
For more: Visit Booz Allen Hamilton
9. Check Point Software Technologies
- Security Engineer
- Head of Harmony Endpoint Security R&D
- Security Engineer, Channel Sales
- Cyber Security Protections Area Manager
- SOC Analyst
For more: Visit Check Point
10.National Security Agency
- Cybersecurity Engineer
- Cryptographic Vulnerability Analyst
- Malware Analyst
- Network Security Engineer
- Cyber Threat Analyst
For more: Visit National Security Agency
Take control of your career and land your dream job
Sign up with us now and start applying for the best opportunities!

What industries can cybersecurity professionals work in?
Cybersecurity professionals can work in a wide range of industries, as virtually every sector today requires some level of cybersecurity expertise. Some of the most common industries where cybersecurity professionals are in high demand include:
- Government: Federal, state, and local governments require cybersecurity professionals to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
- Finance: Banks, financial institutions, and insurance companies must protect financial data and transactions from cyber threats.
- Healthcare: Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers must safeguard patient data and medical records from cyber-attacks.
- Retail: Retailers must protect customer data and financial information from cyber threats.
- Energy and Utilities: Energy and utility companies must secure their systems and networks to prevent cyber-attacks that could disrupt the power grid or other critical infrastructure.
- Technology: Technology companies, including software and hardware developers, require cybersecurity professionals to ensure the security of their products and services.
- Defense and Aerospace: Defense contractors and aerospace companies must protect sensitive government information and technology from cyber threats.
- Education: Schools, universities, and other educational institutions must safeguard student data and research from cyber-attacks.
These are just a few examples of industries where cybersecurity professionals are needed. As more and more businesses and organizations rely on digital technologies and online communication, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals is likely to continue to grow in the future.
10 Popular Cybersecurity Certifications
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP):
CISSP is a globally recognized certification for information security professionals. It validates your expertise in designing, implementing, and managing a comprehensive cybersecurity program.
This advanced certification is for experienced security professionals looking to advance their careers in roles like:
- Chief information security officer
- Security administrator
- IT security engineer
- Senior security consultant
- Information assurance analyst
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
The CEH certification is offered by the International Council of Electronic Commerce Consultants (EC-Council). It validates your understanding of various hacking techniques and methodologies, as well as how to identify and mitigate them.
If you want to develop the mindset of a hacker and adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity, the CEH certification can be valuable.
This certification can be beneficial for roles such as:
- Penetration Tester
- Cyber incident analyst
- Threat intelligence analyst
- Cloud security architect
- Cybersecurity engineer
CompTIA Security+
This certification is offered by the Computing Technology Industry Association (CompTIA) and validates your knowledge and skills in network security, cryptography, identity management, and other related areas.
Acquiring the Security+ certification can be advantageous for various job positions, such as:
- Systems administrator
- Help desk manager
- Security engineer
- Cloud engineer
- Security administrator
- IT auditor
- Software developer
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
Offered by ISACA, the CISM certification is intended for experienced information security professionals who are responsible for developing and managing an organization’s information security program.
Jobs that need the CISM certification include:
- IT manager
- Information systems security officer
- Information risk consultant
- Director of information security
- Data governance manager
Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
The CCSP certification, offered by (ISC)², validates your knowledge of cloud security architecture, design, operations, and service orchestration.
Jobs you can apply for with CCSP certification:
- Product security engineer.
- Cybersecurity solutions architect.
- Application security architect.
- Cloud security engineer.
- Information security auditor.
- Compliance technology specialist.
- Information security manager.
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
The CISA certification, offered by ISACA, validates your expertise in auditing, controlling, and monitoring information systems and IT infrastructure.
Jobs you can apply for with CISA certification:
- Internal auditor
- Public accounting auditor
- IS analyst
- IT audit manager
- IT project manager/auditor
- IT security officer
- Network operation security engineer
- Cybersecurity professional
GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC):
The GSEC certification, offered by the Global Information Assurance Certification (GIAC), validates your understanding of essential security concepts, principles, and technologies.
Jobs that you can look for with GSEC certification:
- Cybersecurity Administrator
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Cyber Security Architect ·
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
The OSCP certification, offered by Offensive Security, is intended for penetration testers and ethical hackers who want to demonstrate their skills in finding and exploiting vulnerabilities.
Jobs you can apply for with OSCP certification:
- Penetration Tester
- Security Analyst
- Offensive Security Engineer and more
Certified Data Privacy Solutions Engineer (CDPSE)
The CDPSE certification, offered by ISACA, validates your understanding of data privacy and protection technologies, processes, and governance frameworks.
Jobs you can get with this certification include:
- NIS Technology Information Security Audit Manager
- Senior Information Technology Auditor
- Cyber Infrastructure SME
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Senior Application Product Security Architect Virtual
Cybersecurity Forensic Analyst (CSFA)
The CSFA certification, offered by the Cybersecurity Institute, validates your expertise in conducting digital forensics investigations, analyzing digital evidence, and reporting findings.
Jobs that you can apply for:
- Cyber Security Forensics Engineer and Data Specialist
- CTOC Engineer Jr
- SOC Analyst/Security Engineer Technical Specialist
- Cyber Security Incident Responder (L5)
- Cybersecurity Forensics Analyst (L4)
Number of US job search results for each certification as of December 2022
Certification | Indeed | Simply Hired | Total | |
CISSP | 159,912 | 14,401 | 8,780 | 183,093 |
CISA | 37,606 | 7,688 | 4,019 | 49,313 |
Security+ | 7,366 | 10,161 | 3,235 | 20,762 |
CEH | 16,402 | 2,425 | 1,468 | 20,295 |
CISM | 8,436 | 4,145 | 2,573 | 15,154 |
GSEC | 4,335 | 3,062 | 2,308 | 9,705 |
SSCP | 4,046 | 3,013 | 2,160 | 11,865 |
CASP | 3,783 | 1,128 | 868 | 5,778 |
GCIH | 3,166 | 2,010 | 1,403 | 6,569 |
OSCP | 2,095 | 1,850 | 946 | 4,891 |
Source: Coursera
Start your Cybersecurity Career Today
With the ever-increasing reliance on digital technologies, security professionals are in high demand across industries. This makes it an opportune time to pursue a career in cybersecurity. Whether you have experience in security practices or possess relevant skills, there are abundant job opportunities available in this field across sectors and industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate is an online program that is designed to provide learners with the foundational skills needed for entry-level cybersecurity roles. The program covers topics such as network security, incident response, security operations, and projects to build practical skills.
The three primary goals of cybersecurity are:
- Confidentiality: It ensures that sensitive information is accessed only by authorized individuals.
- Integrity: It maintains the accuracy and reliability of data and prevents unauthorized alterations.
- Availability: It ensures that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed.
Popular careers in cybersecurity are security analyst, security engineer, chief information security officer, and security consultant.
Some of the top cybersecurity companies are Palo Alto Networks,
Cisco, CrowdStrike, Fortinet, Check Point Software Technologies, and Symantec.

