Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The Statista Report suggests that global cybercrime is expected to exceed $23 trillion by 2027. Thus, the cybersecurity industry has turned to Artificial Intelligence to protect organizational networks and data systems. Just as it has revolutionized other fields, artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in fighting cybercrime. In this blog, let’s see how AI can be used for cyber security.
How can AI be used in Cybersecurity?
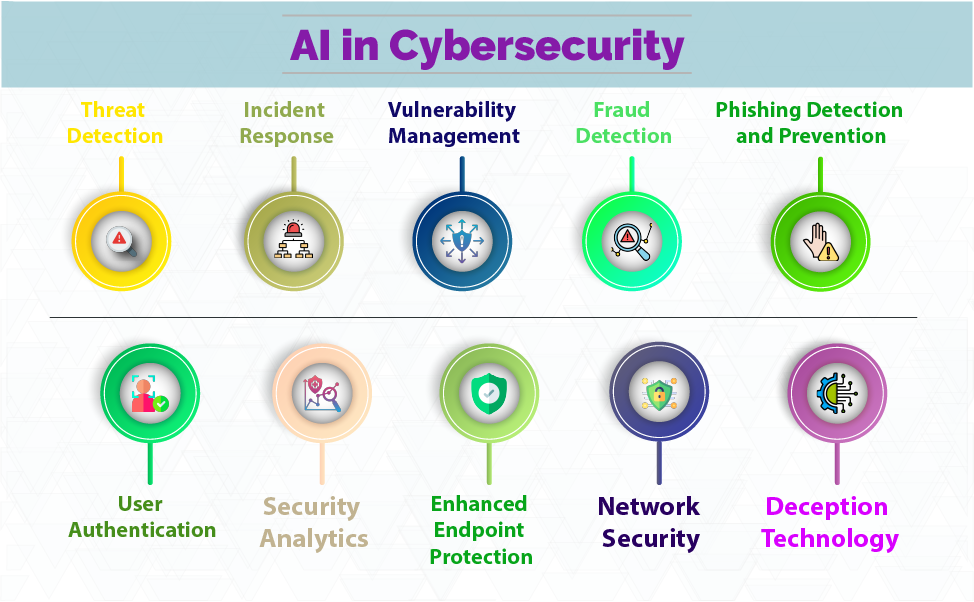
AI can be leveraged in cyber security in several ways to enhance threat detection, response, and prevention. Here are some of the main applications:
1. Threat Detection
AI can significantly improve the accuracy and speed of identifying potential security threats.
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can establish a baseline of normal network behavior and detect deviations that might indicate a security incident.
- Pattern Recognition: Machine learning models can identify patterns associated with known threats and flag similar activities in real time.
- Advanced Malware Detection: AI can analyze files to identify malware based on their behavior and characteristics, even if the malware is new or obfuscated.
2. Incident Response
AI can assist in automating and expediting the response to security incidents.
- Automated Responses: AI systems can automatically execute predefined responses to certain types of incidents, such as isolating affected systems or blocking malicious traffic.
- Forensic Analysis: AI can help analyze a breach’s scope and impact by quickly sifting through logs and data.
- Threat Intelligence: AI can process vast amounts of data from various sources to provide actionable threat intelligence, helping to prioritize responses.
3. Vulnerability Management
AI can help in identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities within systems and applications.
- Predictive Analysis: AI models can predict which vulnerabilities are likely to be exploited based on historical data and current threat trends.
- Automated Scanning: AI-powered tools can continuously scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
4. Fraud Detection
AI can enhance the detection of fraudulent activities, especially in financial systems.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI can track user behavior patterns to detect anomalies that might indicate fraud.
- Real-time Monitoring: AI can process transactions in real-time to identify and block suspicious activities.
5. Phishing Detection and Prevention
AI can enhance the detection of fraudulent activities, especially in financial systems.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI can track user behavior patterns to detect anomalies that might indicate fraud.
- Real-time Monitoring: AI can process transactions in real-time to identify and block suspicious activities.
6. User Authentication
AI can improve the security and efficiency of user authentication processes.
- Biometric Authentication: AI can enhance the accuracy of biometric systems such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition.
- Behavioral Biometrics: AI can analyze patterns in user behavior, such as typing rhythm or mouse movements, to authenticate users continuously.
7. Security Analytics
AI can enhance security analytics by providing deeper insights into security data.
- Big Data Analysis: AI can process and analyze large volumes of security data to identify trends and patterns that might indicate emerging threats.
- Predictive Modeling: AI can build models to predict future security incidents based on historical data and current threat landscape.
8. Enhanced Endpoint Protection
AI can strengthen endpoint security by providing advanced threat protection.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI can monitor endpoint behavior to detect signs of compromise.
- Real-time Protection: AI can provide real-time protection against malware and other threats by analyzing the behavior of applications and processes.
9. Network Security
AI can bolster network security by monitoring and analyzing network traffic.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): AI can enhance the capabilities of IDPS to detect and block malicious activities.
- Traffic Analysis: AI can analyze network traffic to identify unusual patterns that may indicate a cyber attack.
10. Deception Technology
AI can improve the effectiveness of deception technologies used to lure and detect attackers.
- Dynamic Deception: AI can create realistic but fake assets (like honeypots) that evolve to attract and identify attackers.
- Automated Traps: AI can deploy and manage decoy systems and services that mimic real targets to confuse and catch attackers.
By integrating AI into various aspects of cyber security, organizations can improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats more effectively and efficiently.
Challenges in Using AI for Cybersecurity
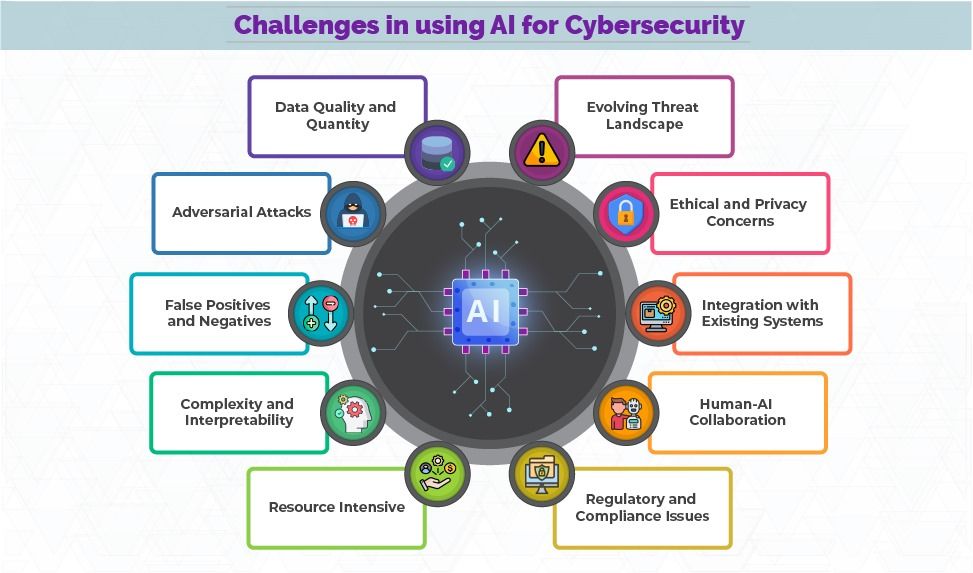
While AI offers significant advantages in enhancing cyber security, it also presents several challenges. These challenges can impact the effectiveness and implementation of AI-driven security solutions. Here are some of the main challenges:
1. Data Quality and Quantity
- Data Dependency: AI models require large volumes of high-quality data for training. Inadequate or poor-quality data can lead to ineffective models.
- Labeling and Annotation: Security data often needs to be labeled or annotated, which can be time-consuming and costly.
2. Adversarial Attacks
- Evasion Techniques: Cyber attackers can use adversarial techniques to fool AI systems, such as modifying malware to avoid detection.
- Model Poisoning: Attackers can inject malicious data into the training set to corrupt the AI model and degrade its performance.
3. False Positives and Negatives
- False Positives: High false positive rates can lead to alert fatigue, where legitimate activities are flagged as threats, causing distractions and unnecessary workload.
- False Negatives: Missing actual threats due to false negatives can leave systems vulnerable to undetected attacks.
4. Complexity and Interpretability
- Black Box Nature: Many AI models, particularly deep learning ones, are complex and not easily interpretable, making it difficult to understand how decisions are made.
- Trust Issues: Lack of transparency can lead to a lack of trust in AI-driven decisions and reluctance to adopt these technologies fully.
5. Resource Intensive
- Computational Requirements: Training and deploying AI models can be resource-intensive, requiring significant computational power and specialized hardware.
- Cost: The development, implementation, and maintenance of AI systems can be costly, which may be prohibitive for smaller organizations.
6. Evolving Threat Landscape
- Dynamic Nature of Cyber Threats: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, requiring AI models to be frequently updated and retrained to stay effective.
- Zero-Day Exploits: AI models may struggle to detect entirely new and previously unknown threats, such as zero-day exploits.
7. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
- Data Privacy: Collecting and using large amounts of data for AI can raise privacy concerns, particularly if sensitive information is involved.
- Bias and Fairness: AI models can inherit biases present in the training data, leading to unfair or biased outcomes in threat detection and response.
8. Integration with Existing Systems
- Compatibility Issues: Integrating AI solutions with existing security infrastructure can be challenging and may require significant changes to current systems.
- Operational Disruption: The deployment of AI systems can disrupt existing workflows and require retraining of staff.
9. Human-AI Collaboration
- Skill Gap: Effective use of AI in cyber security requires specialized knowledge, and there may be a lack of skilled personnel to develop, implement, and manage these systems.
- Human Oversight: Striking the right balance between automation and human oversight is crucial to ensure that AI complements human expertise without completely taking over decision-making.
10. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
- Regulatory Constraints: Compliance with regulatory requirements can limit how AI and data can be used in cyber security.
- Standardization: Lack of standardized practices and guidelines for the use of AI in cyber security can lead to inconsistent implementations and varying levels of effectiveness.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including the development of robust AI models, continuous monitoring and updating, collaboration between AI and human experts, and adherence to ethical and regulatory standards.
Also Read: TOP 10 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE COMPANIES
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best
Apply for top global job opportunities today!
Companies using AI for Cybersecurity

CrowdStrike: CrowdStrike offers an autonomous threat detection and response platform, leveraging AI to detect and prevent cyber threats.

Cybereason: Specializing in endpoint security, Cybereason uses AI to protect against malware, ransomware, and other threats.

SparkCognition: This company focuses on AI-driven security solutions, including threat detection and predictive analytics.

Tessian: Tessian uses machine learning for email security, detecting phishing attempts, and preventing data breaches.

Palo Alto Networks: Palo Alto Networks incorporates AI into its network security products, enhancing threat prevention.

Check Point Software Technologies: Check Point utilizes AI for threat prevention, intrusion detection, and network security.

Darktrace: Darktrace is a leader in autonomous cyber AI, providing real-time threat detection and response. Darktrace employs an Enterprise Immune System that mimics human immune aspects to identify and combat cyber threats.

Fortinet: Fortinet’s Security Fabric platform integrates AI for large-scale enterprise security.

Anomali: Anomali offers threat intelligence solutions, using AI to identify and analyze security threats.

Vectra AI: Vectra specializes in network detection and response, using AI to detect and mitigate cyber threats.
These companies enhance security, automate threat detection, and protect data and networks using AI-powered solutions.
Also Read: HOW TO START A CAREER IN CYBERSECURITY
Is AI Effective in Combating Cyber Crime?
The arrival of AI in our world is like a double-edged sword. On one side, it has created new types of cyber-attacks. On the other, it has bought new security solutions that greatly improve cybersecurity. Using AI technology allows security experts to be proactive in stopping security threats, instead of reacting when it’s almost too late. AI is more efficient than human security analysts in some ways. This makes AI a very useful helper, giving the team more time and energy to handle security threats that need human intervention
As with all past technological advances, some people will use them to cause harm. But every cloud has a silver lining. In cybersecurity, AI will do more good than bad. So let’s support the efforts to create a safer digital world. If you are a cybersecurity engineer looking for a job, then sign up with us now!
Take control of your career and land your dream job
Sign up with us now and start applying for the best opportunities!

Frequently Asked Questions
The future use of AI in cyber security includes more advanced predictive analytics, automated threat hunting, and enhanced protection against sophisticated attacks through machine learning.

