Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Cloud computing is one of the most revolutionary technologies in today’s high-speed groundbreaking innovations. Cloud computing solutions are reshaping the digital landscape by offering unparalleled innovation and collaboration. As a cloud computing expert, you have the power to help organizations operate with agility, reduce costs, and focus on what truly matters: driving growth and delivering value. Let’s delve into cloud computing, understand this technology, its benefits, and why it is an essential component of any forward-thinking business strategy.
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best
Apply for top global job opportunities today!
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, such as including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. Before cloud computing, organizations and people were heavily dependent on local infrastructure, on-premises hardware, and physical storage to access and manage computing resources. Cloud computing allows for faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. It offers scalable and flexible computing resources on the cloud that free users from the need for on-premises infrastructure. In simple words, cloud computing allows businesses to pay attention to growth and innovation.
Types of Cloud Computing Models
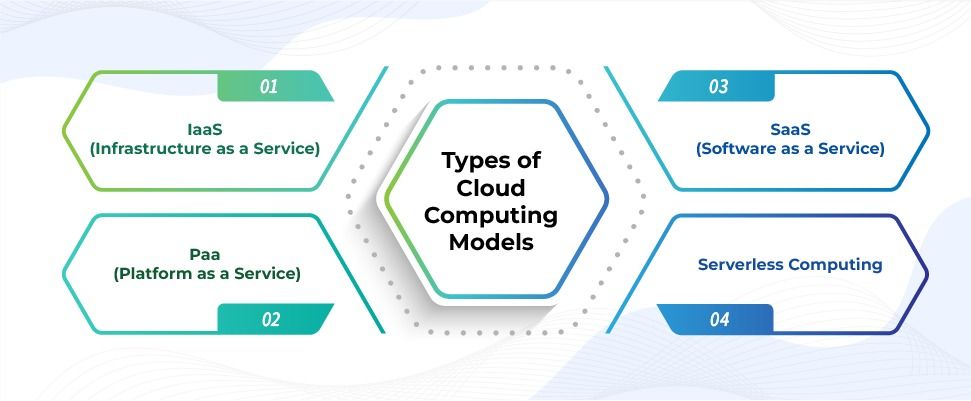
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS offers scalable and virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking over the Internet. Users have full control over the infrastructure, allowing them to customize and manage virtual machines, storage, and networking components.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS provides a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without handling the underlying infrastructure. It includes tools and services like development frameworks, databases, and middleware, which streamline the application development lifecycle.
Examples: Google App Engine, AWS Lambda, AWS Elastic Beanstalk
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, or update the software locally. Users can access these applications from any device with an internet connection, offering flexibility and accessibility.
Examples: Google Workforce, Salesforce, Zoom
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing abstracts server management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code without managing servers. It automatically scales resources based on demand, reducing operational overhead and costs, and enabling rapid development and deployment of applications.
Examples: Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions, IBM Cloud Functions
Types of Cloud Computing
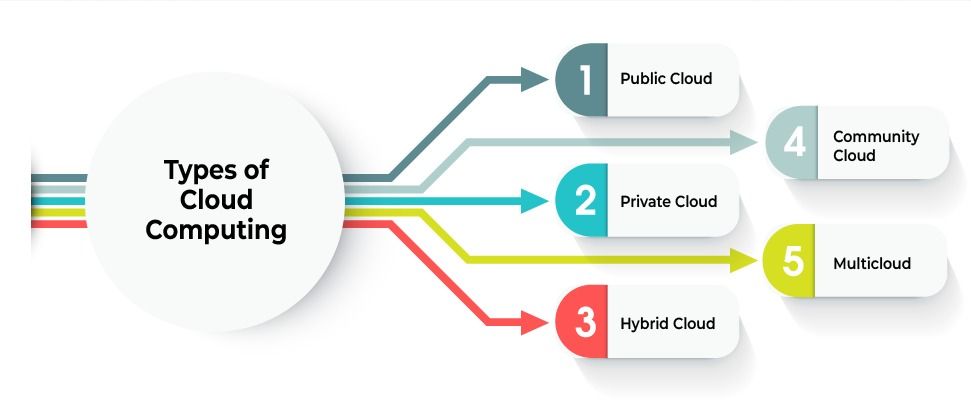
Public Cloud
Public cloud services are delivered over the internet by third-party cloud service providers and can be shared across organizations. Public cloud environments are shared by multiple users, also known as tenants. These services offer scalability and cost-efficiency, as resources are shared among multiple users.
Features
Shared Infrastructure: Multiple organizations share the same cloud resources.
Cost-Effective: You only pay for the resources you use (pay-as-you-go).
Scalability: Easily scale up or down based on demand.
Management: The provider manages all hardware, software, and infrastructure.
Use Case: Startups, small businesses, and large organizations use public clouds for hosting websites, developing apps, or storing large amounts of data.
Private Cloud
Private cloud services are those that are dedicated to a single organization and not shared with others. This is ideal for businesses with sensitive data or regulatory requirements, as it offers more control, privacy, and cloud computing security. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises within the company’s own data center or off-premises via third-party providers.
Features
Dedicated Environment: The entire cloud infrastructure is used exclusively by one organization.
Enhanced Security: Greater control over security and data privacy.
Customization: High levels of customization to meet specific business needs.
Cost: Higher cost than public clouds due to dedicated infrastructure.
Use Case: Government organizations, financial institutions, and healthcare providers often opt for private clouds to meet compliance and security requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
This is a type of cloud deployment model that combines both public and private clouds Combines public and private clouds. Hybrid cloud offers more flexibility as data and applications can be shared between public and private cloud services.
Features
Best of Both Worlds: Combines public and private clouds.
Flexibility: Organizations can choose where to run specific applications or workloads.
Cost-Efficiency: Utilize the public cloud for less sensitive tasks and the private cloud for mission-critical operations.
Seamless Integration: Allows data and applications to flow between environments based on needs.
Use Case: Companies that need to maintain sensitive data in-house while leveraging the public cloud for scaling non-sensitive operations.
Community Cloud
Multiple organizations with similar requirements and concerns share Community Cloud. It can be managed by one of the participating organizations or by a third-party vendor. Community cloud services are useful in sectors where organizations need to comply with industry-specific regulations.
Features
Shared Infrastructure: Multiple organizations with similar goals share resources.
Cost Sharing: Costs are distributed among the community members.
Security and Compliance: Meets industry-specific requirements for data security and privacy.
Use Case: Healthcare, financial services, and government institutions that need to collaborate on shared platforms while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Multicloud
Organizations using multicloud services use multiple cloud services from different providers, which helps in optimized performance. Users can combine services such as AWS Cloud Servers, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud Computing. This approach also helps avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy by distributing workloads across multiple platforms.
Features
Avoid Vendor Lock-In: Greater freedom to choose the best services from different providers.
Increased Redundancy: Enhanced reliability by using different platforms.
Cost Optimization: Select cost-effective services from various providers based on specific needs.
Use Case: Enterprises looking for flexibility in managing workloads, increasing reliability, and optimizing costs.
Read More: Top 12 Cloud Databases in 2024 Key Benefits of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals manage data, run applications, and store information. The flexibility, cost-efficiency, and robust features offered by cloud computing have numerous benefits.
Below are some of the key benefits of cloud computing, which make it a highly attractive solution across industries:
Easy Accessibility
One of the biggest advantages of cloud computing is its easy accessibility. Users can access their data, applications, and services from anywhere in the world as long as they have an internet connection. This fosters remote work, real-time collaboration, and seamless access across multiple devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
Example: Teams can collaborate on projects in real-time, whether they’re in the office or working remotely.
Centralized Data Security
Cloud computing security is often more robust than traditional on-premises solutions because cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. Centralizing data in the cloud helps protect against data loss, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks.
Example: Providers like AWS Cloud Computing and Google Cloud Computing have built-in security protocols to ensure that user data is safe and protected.
Quick Application Deployment
Cloud computing offers unmatched scalability and flexibility. Businesses can easily scale resources up or down depending on their needs. Whether you’re experiencing seasonal spikes in traffic or expanding globally, cloud resources can adjust accordingly.
Example: A retail business can scale its AWS Cloud Servers to handle increased traffic during the holiday season and then scale back afterward.
Enhanced Performance
Cloud computing providers offer state-of-the-art infrastructure that enhances performance by providing high computing power, low-latency networks, and fast data storage options. This ensures that applications and services run smoothly and efficiently, even during high demand.
Example: Cloud providers automatically distribute workloads across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime.
Cost Savings
One of the most significant benefits of cloud computing is its ability to reduce IT costs. Organizations no longer need to invest in expensive hardware, maintenance, or energy consumption. With the pay-as-you-go model, companies pay only for the resources they use, which eliminates the need for over-provisioning and reduces capital expenses.
Example: A company can use cloud hosting to rent server space on an as-needed basis, avoiding the upfront costs of purchasing physical servers.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery in cloud computing ensures that businesses can quickly recover their data and continue operations in the event of a system failure, data breach, or natural disaster. Cloud providers typically offer built-in backup and recovery services, allowing businesses to protect their critical data and minimize downtime.
Example: In the event of a server failure, a business using IBM Cloud Computing can rely on automatic backup and disaster recovery plans to restore operations without major disruptions.
Environment Sustainability
By using cloud computing, businesses contribute to environmental sustainability. Cloud providers optimize their data centers for energy efficiency, and resources are used more effectively due to sharing infrastructure across multiple users. This reduces the overall carbon footprint associated with traditional on-premises IT operations.
Example: Instead of maintaining energy-intensive, underutilized servers, organizations can use cloud computing services that are optimized for efficient energy use.
Must Read: Google Cloud vs AWS: What’s the difference?
How to Choose the Right Cloud Computing Company?
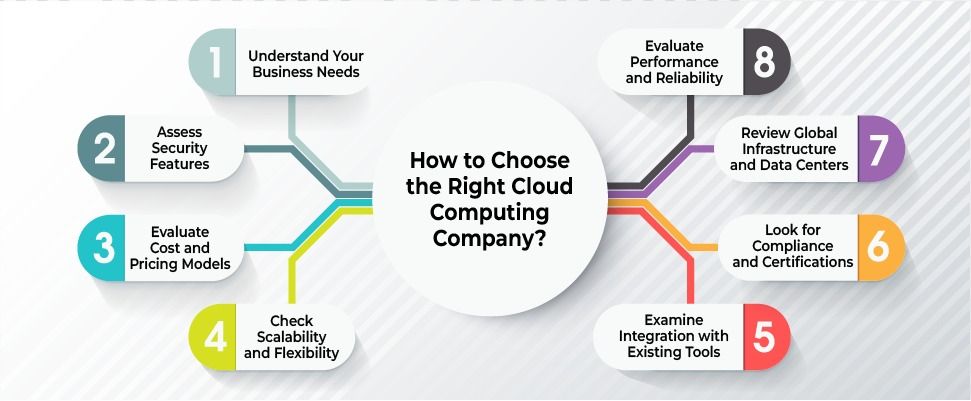
Here are the key factors to consider while choosing the right cloud computing company:
Understand Your Business Needs
It is essential to identify your specific business needs and objectives before selecting a cloud computing company. Determining whether you need IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), or SaaS (Software as a Service) is critical to narrow down your options. For example, a startup developing applications may prioritize providers like AWS Cloud Computing or Google Cloud Computing for their IaaS services, which offer scalable infrastructure.
Assess Security Features
Your cloud service provider should offer robust security measures. This includes encryption, identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication, and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Check if your provider offers built-in security measures, regular security updates, and protection against data breaches. For instance, providers like AWS and IBM Cloud Computing are known for their high-level security features.
Evaluate Cost and Pricing Models
It is important to compare costs and understand the pricing model offered by the different cloud providers available in the market. Different cloud providers offer different pricing structures. These are based on a variety of factors like whether the service is pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, or subscription-based. Most importantly, you must check for hidden costs for data transfer, storage, or additional services. It is important to choose a provider that offers a cost model that aligns with your budget and expected growth. For example, AWS Cloud Servers are flexible with pricing and offer cost-saving options based on usage.
Check Scalability and Flexibility
The right cloud computing service provider will easily be able to offer you the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. Flexible and scalable solutions have the ability to grow with your business, which allows you to adjust computing power, storage, and other resources as needed. For example, Google Cloud Computing provides excellent scalability options, enabling businesses to expand their resources effortlessly during peak times.
Evaluate Performance and Reliability
Providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud Computing typically offer 99.9% uptime guarantees, ensuring smooth operations. A good cloud service provider should offer high performance and reliability, ensuring minimal downtime and fast response times. The provider’s Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and their uptime guarantees can help users check and confirm these details.
Review Global Infrastructure and Data Centers
For businesses that have a global outreach, it makes sense to choose a cloud provider with a robust global infrastructure. It is necessary to confirm that the provider has data centers located in regions where you plan to operate, as this affects latency and data access speeds. For example, AWS and Google Cloud have a global network of data centers, providing low-latency access across different geographic regions.
Look for Compliance and Certifications
Sectors like healthcare, finance, and government rely heavily on confidentiality. Hence, it is important to check industry standards and regulations before choosing a cloud computing service. Ensure that the provider offers compliance with the relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, SOC, PCI-DSS) and industry-specific standards to meet your regulatory needs. Providers like IBM Cloud Computing offer strong compliance with security and data protection regulations for businesses that handle sensitive data.
Examine Integration with Existing Tools
A cloud provider that can seamlessly integrate with your existing tools and software is a great choice. This ensures a smoother migration and avoids costly downtime or compatibility issues. You can look for providers that offer APIs, SDKs, and integration support for your current IT infrastructure. For example, Microsoft Azure may offer better integration with your existing software stack if your company already uses Microsoft products.
Cloud Computing: The Forward-Thinking Business Strategy
Cloud computing is a fundamental shift in how businesses operate today. Rather than looking at it as just a trend, developers and programmers should look at cloud computing as an opportunity to unlock the full potential of cloud technology. Learning the cloud technology essentials — storage, processing power, and applications — and understanding how to use cloud computing to save costs, scale businesses, and enhance collaborations is key to a great professional future. Sign up with Olibr to know more!
Take control of your career and land your dream job
Sign up with us now and start applying for the best opportunities!


