Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best
Apply for top global job opportunities today!
Brief History of AI
The ability of a computer system to perform tasks that involve thinking and doing things like humans is referred to as artificial intelligence (AI). Take any AI-enabled technology, and you will see that it focuses on these components of intelligence: learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and using language.
The years between 1943 and 1952 saw significant progress in AI as artificial intelligence changed from just a concept to an experience that could be used practically. Significant theoretical and technological advancements laid the groundwork for the field during this period. Here is a summary of the events that happened from 1943-1952:
- McCulloch and Pitts’ Neural Network Model in 1943: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pits proposed a model of artificial neurons. In a published paper, they modeled neurons as binary devices that could mimic logical operations, demonstrating that a network of such neurons could compute any logical function. This was a significant step in understanding how biological processes could inspire machine computation.
- Development of Electronic Computers in 1946: The creation of the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) and other early computers, like the Manchester Baby (1948), provided the hardware necessary for AI experiments. These machines enabled the practical implementation of algorithms that could simulate reasoning and learning.
- Norbert Wiener and Cybernetics in 1948: Norbert Wiener introduced Cybernetics, a field that studied control and communication in animals and machines. His work emphasized feedback loops as a mechanism for self-regulation, a concept that became integral to AI and robotics.
- Alan Turing and the Turing Test in 1950: Alan Turing published Computing Machinery and Intelligence, where he proposed the Turing Test as a way to assess machine intelligence. He argued that a machine could be considered “intelligent” if it could mimic human responses well enough to fool a human evaluator. Turing also laid out the theoretical foundations for machine learning.
- Early Machine Learning Attempts between 1951 and 1952: Christopher Strachey and others began experimenting with simple AI programs. Strachey’s checkers program and early attempts at machine learning marked the transition from theoretical ideas to practical applications.
The history of AI reflects an evolution from rule-based systems to data-driven learning models. Today, it impacts industries from healthcare and finance to entertainment and education, proving its transformative potential in addressing complex problems across domains.
Industry-Specific Modern Engineering Solutions
| Industry | Modern Engineering Solution | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | AI-Driven Diagnostics Robotic Surgery |
|
| Construction | Self-Healing Materials 3D Printing |
|
| Automotive & Aerospace | Autonomous Vehicles Lightweight Materials |
|
| Energy | Renewable Energy Microgrids Carbon Capture Technology |
|
| Manufacturing | Digital Twins Industrial IoT |
|
| Agriculture | Precision Farming Vertical Farming |
|
| Education | Virtual Learning Environments AI Tutors |
|
| Smart Cities | Intelligent Traffic Management Smart Energy Grids |
|
| Space Exploration | Autonomous Rovers Space Manufacturing |
|
AI Across Various Engineering Disciplines
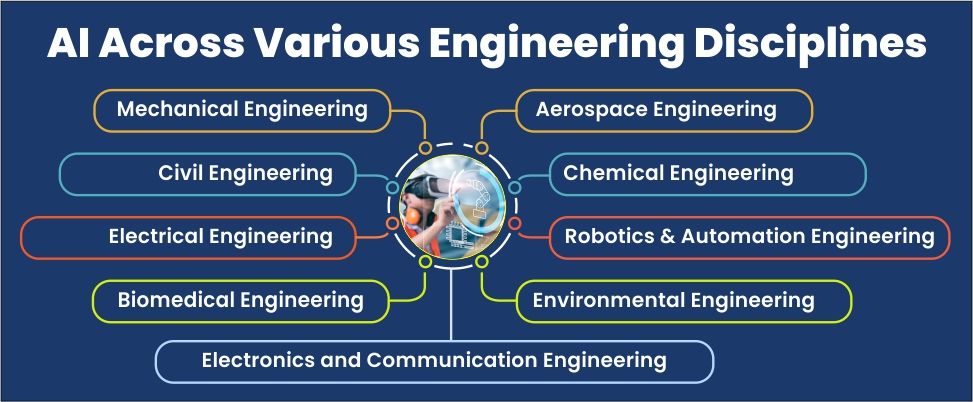
Mechanical Engineering
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze machine data to predict failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Robotics and Automation: AI-driven robots streamline manufacturing, perform quality inspections, and manage complex assembly processes.
- Design Optimization: Generative design tools powered by AI create optimal designs based on specific constraints.
Civil Engineering
- Construction Automation: AI-powered robots assist in tasks like bricklaying and 3D printing of structures.
- Structural Health Monitoring: AI models analyze sensor data to detect and predict structural weaknesses in buildings and bridges.
- Urban Planning: AI tools process vast datasets to optimize city layouts, traffic flows, and environmental impact.
Electrical Engineering
- Smart Grids: AI enhances grid efficiency by predicting energy demand and integrating renewable energy sources.
- Chip Design: Machine learning algorithms accelerate the design and testing of microchips.
- Power System Optimization: AI manages power distribution, reducing waste and improving reliability.
Electronics and Communication Engineering
- 5G and Beyond: AI optimizes network deployment, manages traffic, and enhances user experiences in communication systems.
- Signal Processing: AI improves image, video, and audio signal analysis for better performance in devices.
- IoT Development: AI enables real-time analytics and decision-making in interconnected IoT systems.
Biomedical Engineering
- Diagnostics and Imaging: AI-driven tools analyze medical images to detect diseases like cancer with high accuracy.
- Personalized Medicine: AI models recommend treatments tailored to individual patient profiles.
- Prosthetics and Wearables: AI enhances the functionality of prosthetic limbs and wearable health monitoring devices.
Aerospace Engineering
- Autonomous Systems: AI powers drones and autonomous aircraft for improved navigation and operation.
- Design and Testing: AI tools optimize aerodynamic designs and simulate complex flight scenarios.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI ensures aircraft safety by monitoring and predicting system failures.
Chemical Engineering
- Process Optimization: AI models analyze chemical processes to improve efficiency and safety.
- Material Discovery: Machine learning accelerates the discovery of new materials for energy storage, pharmaceuticals, and more.
- Sustainable Practices: AI identifies ways to reduce waste and energy consumption in chemical manufacturing.
Robotics and Automation Engineering
- Autonomous Robots: AI powers robots that perform tasks in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): AI enables robots to work alongside humans safely and effectively.
- AI in Control Systems: AI enhances robot decision-making, enabling adaptive responses to real-world challenges.
Environmental Engineering
- Sustainability Analysis: AI evaluates environmental impact and suggests sustainable practices.
- Climate Modeling: AI processes vast datasets to predict climate changes and assess risks.
- Waste Management: AI optimizes recycling processes and landfill management.
AI is not only revolutionizing traditional engineering practices but also enabling the creation of entirely new paradigms and solutions across disciplines. The collaboration between AI and engineering continues to open unprecedented opportunities for innovation.
General Challenges Faced by AI

Data Management
AI relies on vast amounts of data for training and operation. Managing, processing, and maintaining the quality of this data becomes increasingly complex. Issues such as data silos, inconsistent formats, and missing information can impede AI applications. For example, in predictive maintenance for manufacturing, poor-quality data may lead to inaccurate predictions, resulting in unnecessary costs or equipment failures. A solution is to implement robust data governance frameworks, employ standardized data collection practices, and ensure interoperability across systems.
Security
AI systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where manipulated inputs can lead to incorrect outputs. Additionally, the reliance on connected systems increases the risk of cyberattacks. An example is automatic vehicles that could be targeted by hackers, potentially causing malfunctions or accidents. Integrated advanced encryption methods, AI-specific cybersecurity measures, and regular system updates can help counter threats.
Privacy
The use of sensitive personal and industrial data in AI raises privacy concerns. Balancing the need for data with ethical considerations is challenging. For instance, AI in healthcare processes patient data, making it vulnerable to breaches or unauthorized use. A solution is enforcing strict data anonymization techniques, complying with data protection regulations, and integrating privacy-by-design principles.
Job Security
Automation and AI-driven systems threaten traditional engineering roles, leading to fears of unemployment and workforce displacement. For example, AI-driven design tools can replace roles traditionally handled by mechanical or civil engineers. It is important to invest in reskilling programs to equip engineers with AI and data analysis skills and create hybrid roles that combine human expertise with AI.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between policymakers, businesses, and educators to create a balanced and ethical implementation of AI in engineering.
AI Applications, Opportunities, and Challenges in 2025
AI is clearly the future, despite many debates around security and data privacy. Let’s look at the various applications, opportunities, and challenges for AI in different sectors:
Healthcare
Applications
- Diagnostics: AI-powered imaging tools like Google’s DeepMind are improving early detection of diseases such as cancer and retinal disorders.
- Personalized Medicine: AI analyzes patient genetics and lifestyle to customize treatments.
- Drug Discovery: Tools like Insilico Medicine accelerate drug research by predicting molecular properties.
- Robotic Surgery: Systems like da Vinci Surgical System use AI for precision in minimally invasive surgeries.
Future Opportunities:
- Predictive analytics will enable early disease outbreak detection and personalized vaccines.
- AI integration in telemedicine will enhance remote patient care.
Challenges
- Ethical concerns in patient data privacy.
- Bias in AI models due to incomplete training datasets.
Autonomous Systems
Applications
- Transportation: Self-driving vehicles (e.g., Tesla Autopilot) optimize road safety and reduce congestion.
- Aerospace: AI assists in drone navigation, aircraft autopilots, and autonomous space rovers.
Future Opportunities
- Fully autonomous urban delivery networks.
- AI-powered air taxis and automated freight systems.
Challenges:
- Regulatory hurdles in adopting autonomous technology.
- Ensuring fail-safe AI systems for critical applications.
Sustainability and Energy
Applications
- Smart Grids: AI balances renewable energy supply with demand, as seen in projects like Google’s AI for wind power optimization.
- Carbon Capture: AI optimizes processes for capturing and storing CO₂.
Future Opportunities
- Climate change modeling to mitigate environmental impact.
- AI-driven energy audits for eco-friendly industrial practices.
Challenges
- High computational energy requirements of AI systems.
- Scalability of AI in underdeveloped regions.
Education and Workforce Development
Applications
- Personalized learning platforms like Coursera’s AI-based recommendations tailor content to individual needs.
- Virtual simulations for skill-based training in engineering and medicine.
Future Opportunities
- AI-enabled career guidance systems.
- Global access to quality education through multilingual AI platforms.
Challenges
- Lack of accessibility to AI tools in low-income regions.
- Resistance to adopting AI-based learning in traditional systems.
Cybersecurity and Privacy
Applications
- Threat detection systems identify and limit cyber risks in real time.
- AI-enhanced encryption methods secure sensitive data.
Future Opportunities
- Predictive cybersecurity that prevents attacks before they occur.
- Biometric AI for secure authentication processes.
Challenges
- AI-driven cyber threats getting too sophisticated to track.
- Balancing user privacy with surveillance needs.
Smart Cities and Infrastructure
Applications
- Traffic management using AI to reduce congestion (e.g., Singapore’s AI-based traffic flow system).
- Predictive maintenance of infrastructure using IoT and AI analytics.
Future Opportunities
- Fully autonomous public transport networks.
- AI-optimized urban planning for sustainable cities.
Challenges
- Integrating legacy systems with AI solutions.
- High initial investment in AI infrastructure.
Creative Industries
Applications
- Generative AI tools like ChatGPT aid in content creation, from artwork to storytelling.
- AI in film editing and music composition enhances production quality.
Future Opportunities
- Interactive AI-generated media experiences.
- Real-time AI co-creation with humans in gaming and art.
Challenges
- Ethical debates on copyright and originality of AI-generated works.
- Over-reliance on AI affects human creativity.
Space Exploration
Applications
- AI-powered rovers (e.g., Perseverance) analyze Martian terrain.
- Autonomous navigation for deep-space probes.
Future Opportunities
- AI-driven asteroid mining.
- Enhanced space habitats with AI managing life-support systems.
Challenges
- Ensuring AI systems function in extreme environments.
- Limited data for training AI models for extraterrestrial applications.
AI: The Future is Here
AI is everywhere, whether it is smartly driven vehicles, predictive data output platforms, or efficiently managed patient systems. One must remember that we all embrace AI with one goal: to upgrade and improve all aspects of life. Of course, every technology comes with its set of challenges. But there is no need to worry, as there are processes and countermeasures already in place to mitigate these challenges. As engineers, what you can do is keep upskilling and stay updated with the latest innovations in the industry. At Olibr, we help you find what you need: the best job, skills assessment, and more. Sign up with Olibr to know more!
Take control of your career and land your dream job
Sign up with us now and start applying for the best opportunities!

FAQs
ChatGPT, Gemini, Anthropic Claude, Perplexity, Zoho SalesIQ, etc, are some
chatbots that have free versions.

