Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
With the increasing data intake today, businesses need a robust database solution. While there are many database options available, PostgreSQL and MySQL stand out as the top open-source relational database management systems that help businesses and backend developers manage data efficiently. In this blog, we will learn the difference between MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best
Apply for top global job opportunities today!
What is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) written in the C language. It supports advanced data types and is highly customizable. Developers can customize it by simply developing any plugins to make it fit the requirements of users. Moreover, it provides great performance, functionalities, and security, and at the same time, it is also user-friendly.
Also Read: Features of PostgreSQL
Why use PostgreSQL?
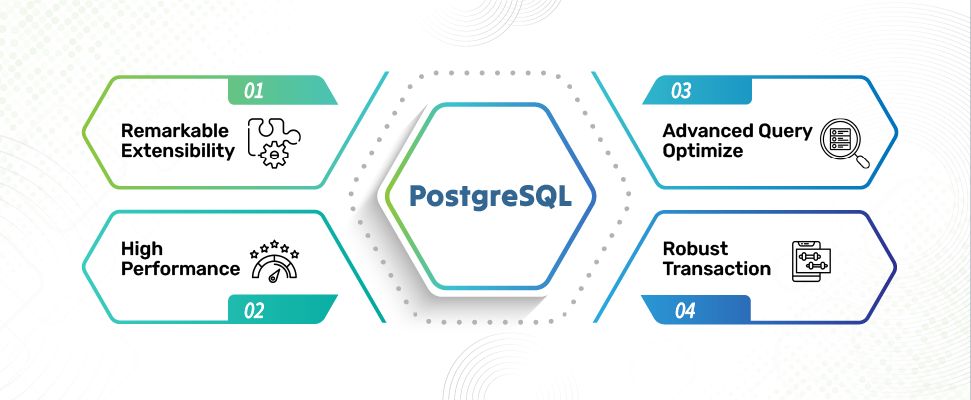
- Remarkable Extensibility: PostgreSQL databases can be customized according to user requirements. It supports a wide set of data types, from custom user-created ones to multiple procedural languages for writing stored procedures. This allows a user to extend the database’s capabilities with custom functions, operators, and new languages.
- High Performance: PostgreSQL’s performance is commendable. It can easily handle huge datasets and concurrent transactions. Complex optimization techniques further make it suitable for high-demand settings. Its architecture allows users to horizontally scale the apps, partition, and replicate effortlessly with rising volumes and user traffic.
- Advanced Query Optimize: PostgreSQL’s advanced query optimization enables the efficient execution of complex queries. It supports index-only scans, bitmap heap scans, and genetic query optimization to reduce query execution times. Due to this, PostgreSQL databases are used for data analysis and business intelligence applications requiring fast and accurate data retrieval.
- Robust Transaction: This ensures PostgreSQL’s data integrity and consistency through full ACID compliance and multiple transaction isolation levels. This further protects data against anomalies and guarantees reliable transaction processing, even in complicated and multi-user setups.
Must Read: PostgreSQL vs. MongoDB: Key Differences
What is MySQL?
MySQL is an open-source database management system (DBMS) that uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to manage databases. MySQL is used by many web applications to store data such as usernames and passwords. MySQL is also used by some content management systems (CMS), such as WordPress and Joomla.
Why use MySQL?

MySQL is widely used in many industries and businesses of all sizes. The following are reasons why you should use MySQL:
- Compatible with Other Technologies: MySQL was designed with interoperability in mind; due to this, it can integrate with PHP, WordPress, Java, Perl, Joomla, and C++. It also runs well with Mac OS and Windows. Besides, it can deploy vast amounts of data into a virtual environment or be distributed and centralized.
- High Security: MySQL is known for its high security and reliability, due to which popular web applications including WordPress, Facebook, and Twitter have used MySQL until now. The data security and support for transactional processing that accompanies the recent version of MySQL can greatly benefit any business.
- Structured Data: MySQL stores data in a structured and organized manner in a well-defined schema. This allows MySQL to better optimize actions like data retrieval, updating information, or more complex actions like aggregations. This schema helps define the structure and relationships between the different tables.
- Unmatched Scalability: MySQL’s high scalability makes it suitable for apps that integrate into multiple systems but consume fewer resources. This open-source solution gives high flexibility for customizing eCommerce businesses with unique database server requirements.
PostgreSQL vs MySQL: Key Differences
| Factors | PostgreSQL | MySQL |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Object-relational database | Relational Database |
| Data types | Provides a wider range of data types, from advanced to custom, JSON, and more | Limited sets of data types |
| Indexes | Partial indexes, B-tree indexes, hash indexes, and Expression indexes | R trees, B trees, and hash indexes |
| Concurrency | Supports advanced features of Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC), which allows concurrent access | Supports concurrency control but may not have the robust support of PostgreSQL |
| Case-sensitivity | Case sensitive in most cases | Case insensitive |
| Supported Language | Erlang, Tcl, JavaScript, .NET, R, C++, C, JSON, Python, Java, Go, and Delphi | Perl, Lisp, Delphi, Node.js, Erlang, C, C++, R, and PHP |
| Replication | Provides synchronous replication | one-way asynchronous |
| Speed | Faster with read-write operations, massive datasets, and complicated queries | Faster with read-only commands |
| Troubleshoot | Hard to troubleshoot | Easy to troubleshoot |
| Extensibility | Highly extensible and supports various advanced data types | Extensible only with basic numeric and character data types |
| Security | native window services, PAM, and LDAP | IP-based client authentication and filtering using Kerberos and PAM |
| User Interface | PgAdmin | Workbench |
| Performance | Shows high performance while working with heavy data | Shows high performance while reading data |
| Suitable for | Complex operations and custom conditions | Web operations, content operation systems |
| Data Support | Supports user-defined types, arrays, hstore, and XML | Supports JSON, Key-value pa |
| Native Server | Supports the Transport Layer Security (TLS) | Supports the Server Sockets Layer (SSL) |
| Community Support | Boasts a large helpful community that has detailed PostgreSQL documentation | Mature and large community with free and 24/7 paid support |
Also Read: SQL vs. JSON: Key Difference
PostgreSQL vs. MySQL: Querying Differences
- Query to Increase the Column
MySQL uses AUTO_INCREMENT to create an auto-incrementing column in a table:
CREATE TABLE mytable (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255)
); Whereas, PostgreSQL uses SERIAL to increase the column:
CREATE TABLE mytable (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255)
); - Timestamp Literals
MySQL uses single quotes. The following is the query:
SELECT * FROM mytable WHERE created_at = '2024-05-13 12:00:00'; PostgreSQL uses the TIMESTAMP keyword along with it. The following is the query for PostgreSQL:
SELECT * FROM mytable WHERE created_at = TIMESTAMP '2024-05-13 12:00:00'; - Query for Concatenation
MySQL uses CONCAT, the following is the query:
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) AS full_name FROM employees; PostgreSQL uses | | operator for concatenating two strings.
The following is the PostgreSQL command:
SELECT first_name || ' ' || last_name AS full_name FROM employees; - String Quotes Difference
MySQL uses single quotes (‘) for string literals. The following is the query to use single quotes in MySQL:
SELECT * FROM emptable WHERE name = 'Ansel'; However, in PostgreSQL, single quotes (‘) or double quotes (“) are used for string literals, and these quotes behave differently. The following is the query:
SELECT * FROM emptable WHERE name = 'Ansel';
-- or
SELECT * FROM emptable WHERE name = S"Ansel"; - Limiting Rows
PostgreSQL uses LIMIT and FETCH FIRST to limit rows. The following is the query:
SELECT * FROM mytable FETCH FIRST 18 ROWS ONLY; While MySQL uses only LIMIT
SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 18;SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 18; PostgreSQL vs. MySQL Real-World Use Cases
| PostgreSQL | MySQL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
 | Apple uses PostgreSQL to handle its company database. |  | Amazon uses MySQL for its ACID properties and to store its customer details, and product catalog. |
 | Twitch 125 database platform is fully managed by PostgreSQL. |  | Facebook uses MySQL for its compatibility, flexibility, and cost-effective options. |
 | Instagram uses PostgreSQL to handle its billions of data. |  | Uber uses MySQL to analyze the ride patterns and market trends. |
 | NASA uses PostgreSQL to store the data on the orbit and then replicate that database on the ground. |  | Pinterest uses MySQL to manage vast user-generated content and analytics. |
 | Spotify uses PostgreSQL to handle its 71 million monthly users and 50 million songs. |  | Udemy uses MySQL for its reliable transaction process for course enrollment. |
 | IMDB uses PostgreSQL to analyze and process its huge database, which contains over 6 million movies. |  | Airbnb uses MySQL for accommodation and managing the payment process. |
Also Read: Top 10 Database Management Systems in 2024
PostgreSQL vs. MySQL: Which Database Solution Is Best for Businesses in 2024?
PostgreSQL allows backend developers to perform advanced operations using various index types and custom data types. It also supports different programming languages like Python, Perl, and C within the database. The ACID principles provide secure and reliable transmissions. This makes PostgreSQL a versatile choice for handling complex datasets. Therefore, PostgreSQL is beneficial for businesses that require extensive data manipulation or want to customize their business logic. Due to this, PostgreSQL is best for complex and large-scale applications.
In comparison to PostgreSQL and other databases, MySQL has a simple design that makes it suitable for building apps within an organization. This simple design further promotes easy comprehension and maintenance. Because of this simplicity, MySQL is perfect for static systems that do not deal with complex data manipulation or multi-faceted transactional operations. However, MySQL is best known for its efficient read operations, due to which it is best for apps that require quick retrieval. Apart from that, MySQL is best for small-scale applications, basic data reporting systems, websites, and content delivery networks.
In summary, choose PostgreSQL for complex and large datasets, and pick MySQL if you want a simple database architecture for small-scale applications. If you want to hire a PostgreSQL developer or a MySQL developer, then sign up with Olibr now!
Take control of your career and land your dream job
Sign up with us now and start applying for the best opportunities!

FAQs
To perform an update query in PostgreSQL, use the UPDATE statement. The following is the query:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE condition;
A MySQL online compiler is a web-based tool that allows users to test queries, experiment with them, and troubleshoot them directly from their web browser.
MySQL commands are the instructions used to interact with the database management system. These commands are based on data retrieval, data manipulation, and data creation and deletion.
To delete a table in MySQL, you can use the DROP TABLE statement. The following is the command:
DROP TABLE table_name;
To check the MySQL version, use the SELECT Version(); query in the MySQL client. This query returns the version number of the MySQL server you are connected to.

