Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Angular and Vue have gained immense popularity in recent years. Angular for their comprehensive features, and Vue for their progressive offerings.
According to a recent GitHub statistics, Angular has cultivated around 41000 stars and 730 contributors. And on the other hand, Vue has gained over 114000 stars with only 193 contributors. This makes Vue a rising star with 135 stars per day while Angular only gets 37 stars on average.
However, that doesn’t necessarily mean Angular’s popularity is declining! In fact, Angular with comparatively fewer stars with higher contributors means a larger contributor base. This article, today will walk you through a detailed comparison of Angular vs. Vue. So let’s dig into it!
What is Vue?

Vue is an open-source progressive JavaScript framework known for its clear and concise syntax. It is used for single-page web applications without the need for extensive configurations. Moreover, its lightweight nature makes it a great choice for building small and mid-sized applications.
Key Features of Vue
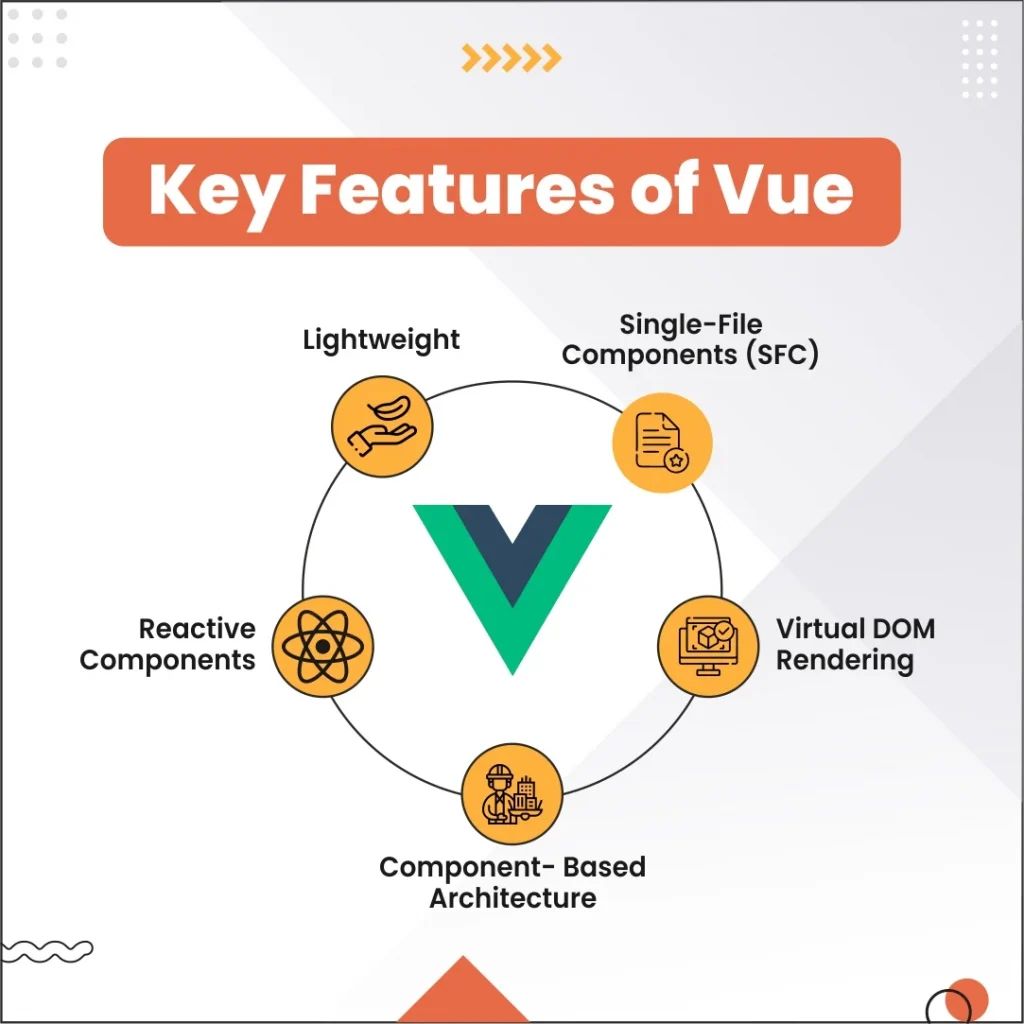
- Single-File Components (SFC): It eliminates the multiple files per component strategy and lets the developer define HTML, CSS, and JavaScript within the single file. As a result, it promotes faster and more efficient development.
- Virtual DOM Rendering: This direct manipulation of virtual DOM improves performance speed and significantly reduces the number of updates.
- Component-Based Architecture: Instead of lengthy code, this type of architecture breaks down applications into smaller reusable components. Due to this, each element works independently without disturbing other segments of applications. This feature comes in very handy while developing large apps process.
- Reactive Components: It uses two-way data binding between a component’s state and the Document Object Model (DOM) that scales up the development process. This feature is beneficial in handling some complex front-end applications with automatic synchronization within the components.
- Lightweight: It can smoothly load powered applications even in a slow network connection boosting the user experience.
Pros & Cons of Vue
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy migration | Two-way binding can cause rendering issue |
| In-built solution for easy state management | Language barrier for English-speaking developers as most of the documentation is written by Chinese developers. Vue has large community of users from China. |
| Lightweight and fast | Limited support for large projects |
| Improved performance and optimization with updates | Does not offer enough plugins and tools |
| Default update for bugs | Excessive flexibility can complicate the project |
| Flexible function-based API for component logic | Integrating into a huge project can be difficult |
| Robust production environment | Lacks compatibility with external tools and frameworks |
Companies that Use Vue

Don't miss out on your chance to work with the best!
Apply for top job opportunities today!
What is Angular?

Angular is used to build enterprise Single-page Web Applications (SPAs). It promotes a modern MVVC framework and uses HTML and TypeScript. It implements core and optional functionality as a set of TypeScript libraries whenever users import them into apps.
Features of Angular
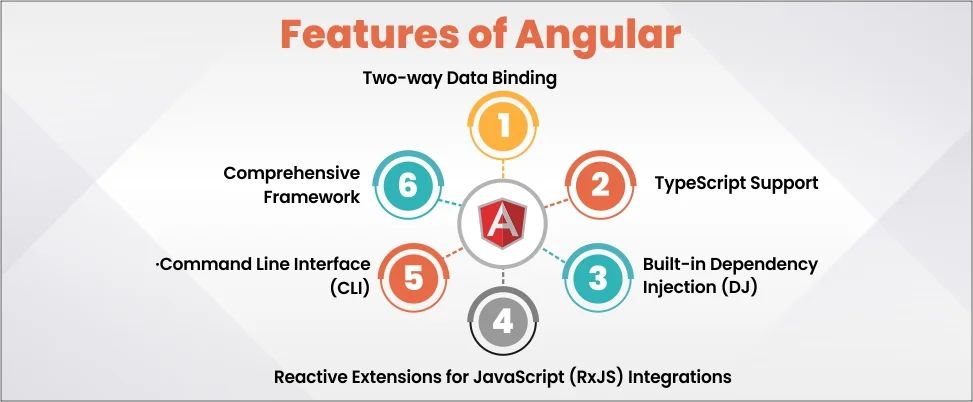
- Two-way Data Binding: It minimizes the need for DOM manual manipulation and synchronizes the view and model layers seamlessly. Because of this, changes are automatically updated in the view and save development time.
- TypeScript Support: This feature catches errors at compile time and provides high code quality, robust tooling support, and enhanced maintainability.
- Built-in Dependency Injection (DJ): It manages dependencies in the code and allows developers to concentrate on component logic.
- Command Line Interface(CLI): It supports SCSS features, routing, and commands like ng new and ng add that simplify integration and discovery of pre-defined features.
- Reactive Extensions for JavaScript (RxJS) Integrations: It can handle asynchronous operations with ease and efficiency.
- Comprehensive Framework: This feature provides extensive built-in features to handle routing, forms handling, and HTTP clients.
Pros & Cons of Angular
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Advanced features lead to high-performance | Limited SEO |
| Smooth third-party integration and customization options | Code verbosity due to component-based architecture |
| TypeScript offers refactoring services, navigation, and autocomplete, eliminating errors within code | Simple applications can grow larger with repetitive code |
| Easy integration of elements from other frameworks | Complex migration from Angular.js to Angular |
| CLI provides timely recommendations for plugins and dependencies | DJ dependency can make the codebase complex |
| Robust tool to build enterprise-scale app | Steeper learning curve with each release |
| Long-term Google support and detailed documentation | Larger bundle sizes impact initial loading time on slow network |
Companies that Use Angular

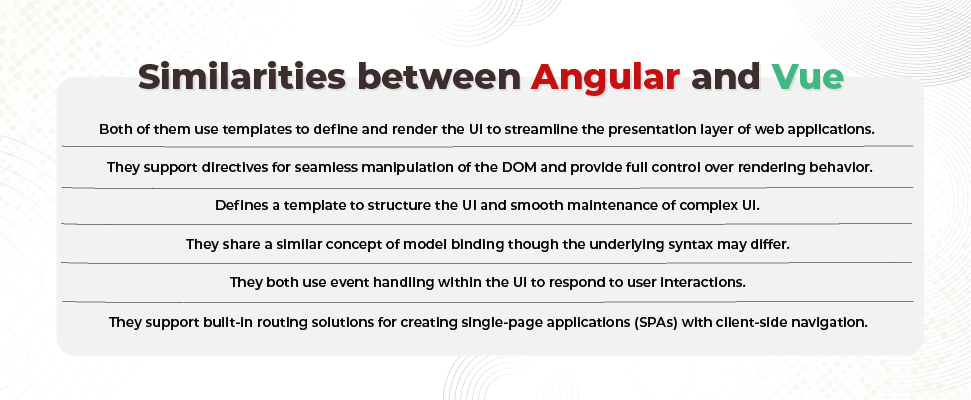
Similarities Between Angular and Vue
During the development phase, Vue inherited certain principles and ideas from Angular due to which Vue and Angular shares common concepts and fundamentals. This can undoubtedly help developers with prior knowledge of Angular to make a switch to Vue and also, leverage Angular skills while working with Vue.
Difference Between Angular and Vue
The table outlines the key differences between Angular and Vue
| Factors | Angular | Vue |
|---|---|---|
| Backend Compatibility | Compatible with Java and PHP in back-end development | Dedicated to front-end development only |
| Source Language | TypeScript | JavaScript and Typescript |
| Full feature JS/Progressive JS | Fully JavaScript Framework | Progressive JavaScript Framework |
| Application Size | Lightweight typically ranges between 50 KB and 100KB | Mid to large size that ranges between 250 KB to 563 KB |
| State Management | Uses Angular Reactive Extension (NgRx) for large apps | Uses VueX to handle complex apps |
| Code Syntax | With the concept of decorators and injectors, code syntax becomes complex | Straightforward and simpler syntax |
| Scalability | Provides good scalability due to its full-fledged framework | Lacks pre-defined tools and thus creates complexity in dealing with large codebase |
| Components and Extensibility | Offers structured and well-designed app architecture | Greater flexibility and customization options |
| Developed By | Evan You | |
| Data Binding | Two-way data binding and support asynchronous services | One-way data flow in components |
| Built-in Libraries | Built-in RxJS and CLI | Relies on third-party tools and libraries |
| Security | Cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site script inclusion(XSSI), and cross-site request forgery (XSRF) | Built-in defense features such as HTML content filtering and attribute binding |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible | Not flexible need to follow the rule |
| Debugging and Testing | Provides tools like Karma and Jasmine for robust testing methodology | Lacks comprehensive tools |
Why Use Vue?

Its small size is the major added advantage that not only improves the overall performance but also promotes faster load times. Also, the perfect balance between fast development and efficient execution on the web directly enhances the user’s experience.
In terms of code complexity, it is relatively easier than Angular, making it an excellent choice for novices. Besides, it is versatile enough to handle single-page and complex applications. Lastly, its well-documented features and guidelines help developers with the basic knowledge of JavaScript and HTML to quickly get started with a smooth Vue development experience.
Why Use Angular?

TypeScript detects any type of error in the early stage, this contributes to high-quality code and reduces potential issues. Secondly, Angular’s robust ecosystem of plugins and add-ons is a boon for developers to enhance their productivity. Additionally, the Model-View Model (MVM) architectural pattern allows separate collaboration on different sections of the same app. Finally, Angular provides comprehensive documentation through which developers can access all the information that they need while developing the application. Nevertheless, going through this extensive documentation might take a longer time to learn.
Final Words
In this dynamic world of web development, one right choice can tremendously impact the success of any kind of project. So you must carefully weigh their pros and cons as well as the features of these two frameworks. Angular and Vue are the two popular JavaScript frameworks, Vue uses a component-based approach and offers simplicity and flexibility. Whereas, Angular offers comprehensive architectural patterns with in-built support of dependencies injection, making ideal choice for large applications. Your final choice of these frameworks lie solely on the preference of your development team, and of course, on project requirements. If you are looking to hire Angular developers or Vue developers, sign up with Olibr now!
Take control of your career and land your dream job!
Sign up and start applying to the best opportunities!

FAQs
There is no clear-cut answer to this question as it varies on different factors like team expertise and project requirements. Both of these frameworks come with weaknesses and unique strength.
Angular has a large developer community so finding Angular developer is far more easier than finding a Vue developer.
Vue promotes faster development and prototyping due to its lightweight.
Undoubtedly, Angular! Its built-in functionalities, scalability features, and robust ecosystem are enough to build large applications.
Angular and Vue both don’t compromise on security, but neither can guarantee security unless you implement proper development practices. Therefore, you must understand how to handle user input and properly implement its best practices.

